What is Virtual Reality?
Virtual Reality (VR) is a computer-based, interactive, multisensory simulation environment that occurs in real time. It provides users with opportunities to participate in activities within environments that appear similar to real-world objects and events.
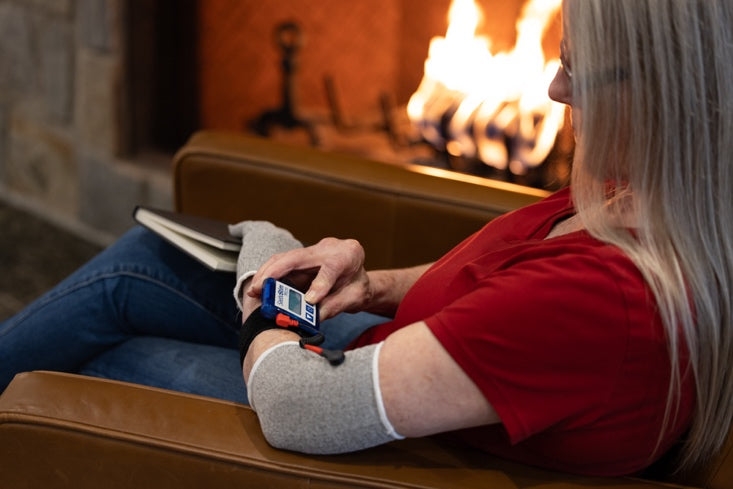
Virtual Reality has emerged as a new treatment approach in stroke rehabilitation settings over the last ten years. Recent evidence indicates that intensive massed practice can stimulate recovery of motor skills in patients following stroke. VR may be useful to augment rehabilitation of the upper and lower limb in patients suffering from stroke and other neurological injuries.
Power of Presence. Are you in or out?
There are 2 major VR categories that determine the degree of presence or level of immersion within the environment.

Immersive
The user has a strong sense of presence. The virtual environment is delivered by equipment worn by the user or the person is situated within a virtual environment. Full immersive systems use head-mounted displays, special gloves, and large concave screen projections to create the sense of immersion.
Non-immersive
Usually two-dimensional and delivered through a computer screen. The user controls devices such as a joystick, mouse, or sensors.
Improve Your Performance. Virtually.
Virtual Reality has been shown to be an effective therapeutic option for neurologically involved clients. Below are key areas of recovery that are challenged through the use of VR systems:
- Sensory
- Visual/Perception
- Cognition
- Motor
- Communication
- Emotional
- Social
- Pain



