What is Cortical Priming?
Improved outcomes are associated with increased excitability of the affected hemisphere. Interventions that focus on re-balancing the communication between both hemispheres are likely to lead to improved recovery.
Priming is a technique used to enhance the brain’s ability to re-balance the 2 hemispheres following a stroke. Priming interventions include invasive and non-invasive techniques and can be administered prior to or during therapy.
Rebalance and Restore.

Uneven Playing Field
The brain consists of 2 hemispheres each responsible for controlling the opposite side of the body. Normally, each hemisphere inhibits the opposite side to avoid mirror movements (both sides performing same movement simultaneously).
After a stroke, the 2 hemispheres experience an unbalancing of both sides with the unaffected hemisphere receiving more signals than the affected hemisphere. This imbalance leads to increased excitability and decreased inhibition to the healthy side.
Do Not Enter
Imagine a road with a detour sign alerting drivers to turn right instead of left. Although the drivers would like to go left, they are directed to turn right. In this example, the drivers are the signals and turning right is the unaffected hemisphere whereas turning left is the affected hemisphere.
Continued decreased signals (excitability) to the affected hemisphere has been shown to result in limited functional recovery. The goal of therapy is to figure out ways of eliminating the detour sign and making the path to the left (affected side) more passable.

Stimulate Recovery
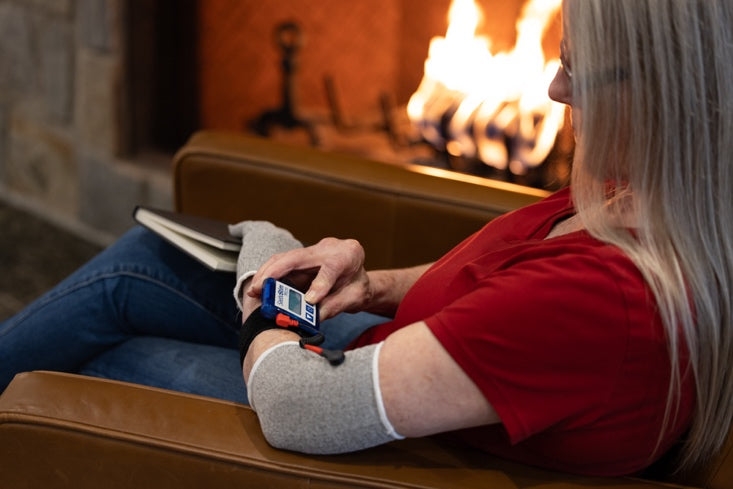
Sensory electrical stimulation is an example of a safe, non-invasive technique used to improve cortical excitability of the affected side of the brain. By priming the brain, prior to or during functional training, cortical plasticity and rebalancing of the hemispheres may result leading to better functional outcomes.



